New projects to boost Earth Observation data capability

The UK Space Agency has announced two new projects to enhance Earth Observation Data Capability.

The UK Space Agency has announced two new projects to enhance Earth Observation Data Capability.

As the ERS-2 climate mission starts its burn up in the Earth’s atmosphere, our Space Exploration Special Adviser Sue Horne talks about how the mission has spanned her career in space.

Imperial College London's Professor Helen Brindley explains how the ESA FORUM mission, contracted to Airbus, will improve the accuracy of climate change forecasts and help scientists see the Earth through new eyes.

It's not every day I attend a workshop where satellites, bananas, livestock, and ethics are central to the conversation.
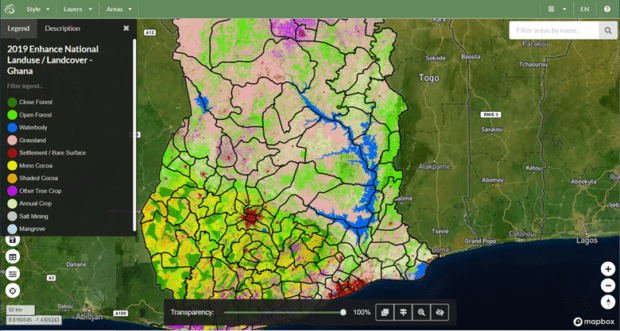
Monitoring cocoa plants in Ghana from space Globally, the majority of tropical deforestation is still linked to commodity farming and production. The expanded production of agricultural commodities such as beef, soy, cocoa, palm oil and paper/pulp are the major drivers …
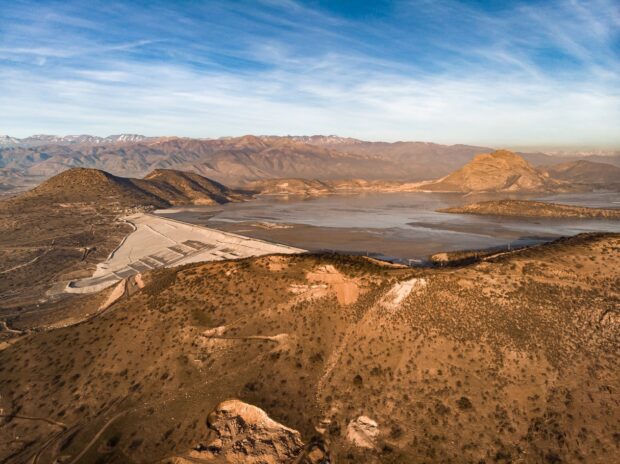

New satellite-driven tech is being used to improve dam safety in Peru.
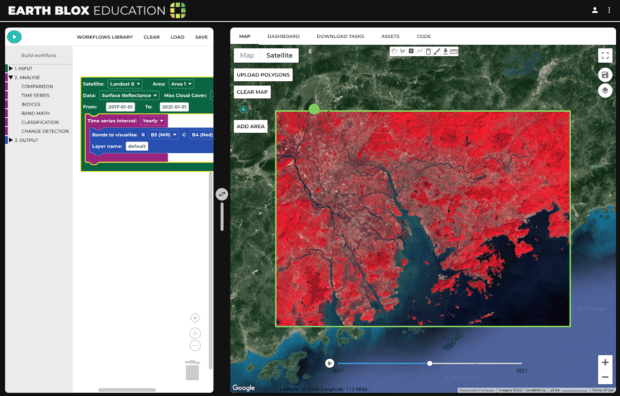
My dissertation used Earth observation satellite data. But I didn’t know how to code.

17 students across the UK have begun their PhD training this month as part of a new Earth Observation Centre for Doctoral Training

The International Charter: Space and Major Disasters, better known as the Disaster Charter, was formed on 20 October 2000 by the European Space Agency (ESA), French Space Agency (CNES) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), with the UK joining in …
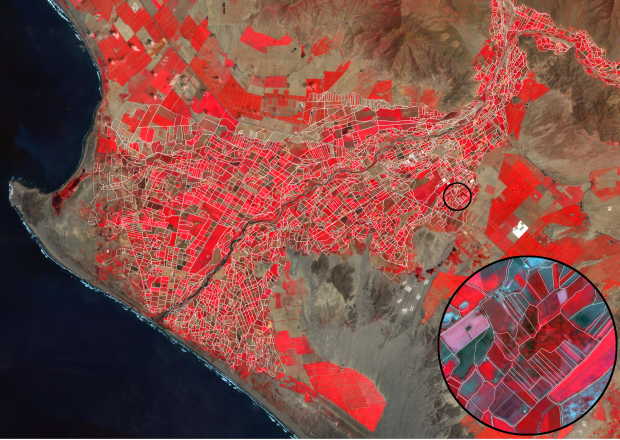

How one of our projects uses satellites to help solve disputes over water in northern Peru.